When you spend the day working with industrial machinery, you depend a lot on good, high-quality AC and DC motors. Motor breakdown can happen for a variety of reasons, and the mean failure rate among industrial plants is around 3.4% per unit per year with a range of variation – quite low, though there will be breakdowns all the same. If your motors need repair or fail, your business must be able to rely on its repair facility for effective electric motor repair to have them operational as soon as possible.

At Industrial EQ Diagnostics.INC, we deliver comprehensive AC/DC electric motor repair services to clients. Our industrial electric motor repair processes operate as we demonstrate to help your company's motors through these methods.
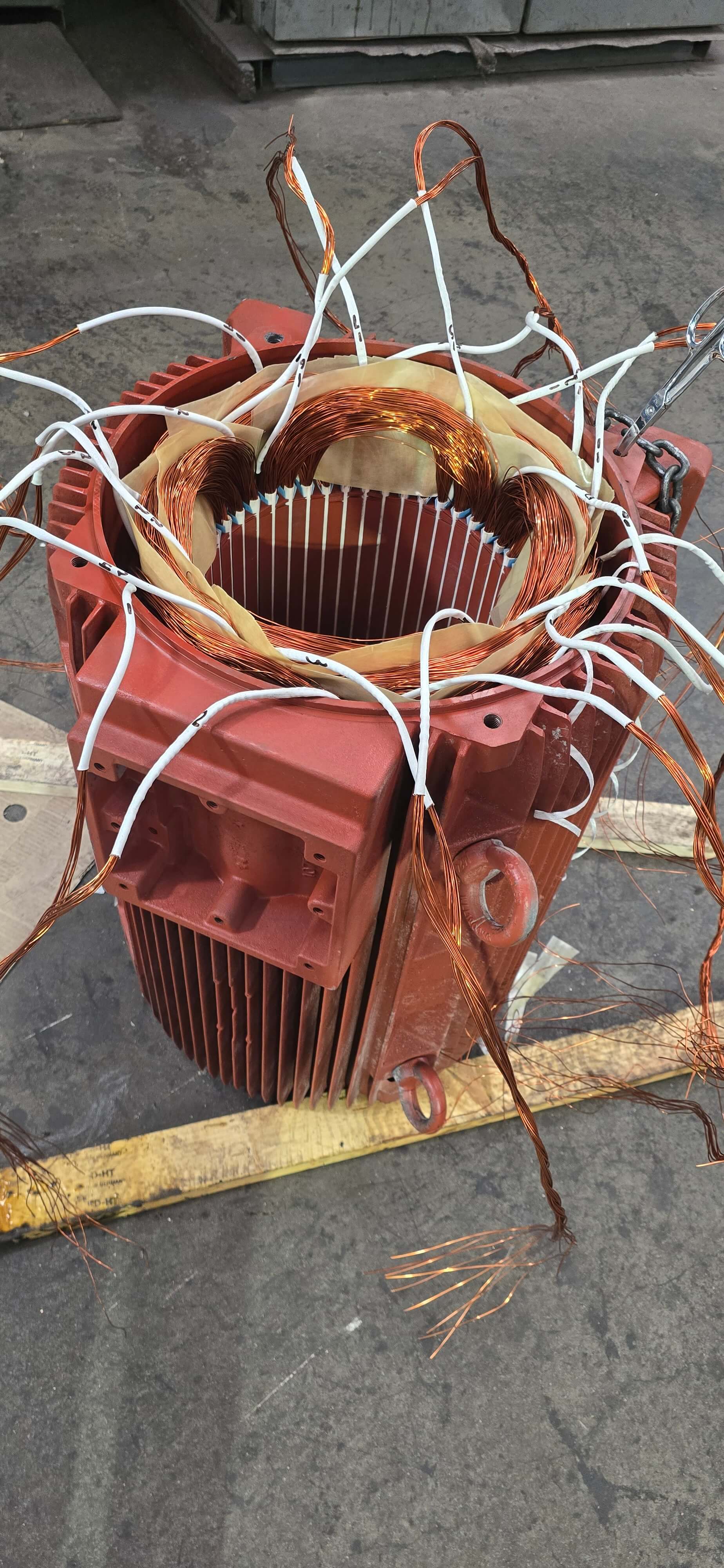
Very few machine shops have in-house rewinding, but we do. We've continuously improved our rewinding method in the years past to provide you with the optimum repair service. Our skilled winding engineers have the ability and infrastructure to rewind industrial motors of all types, including AC, DC, servo, and spindle motors. Most motor shops rewind only up to a specific horsepower or work on a limited type of motor. We do not have this limitation and can rewind all forms, such as random, concentric, lap, form coil, and armature rewinds.
Most motor failures are caused by the bearings. The bearings, by their very name, support a large amount of the mechanical load in a motor. They have to deal with high friction and withstand massive force. Due to these pressures, the bearings wear out faster than most other motor parts. Bearing maintenance is crucial in a motor, and because of this, it's standard procedure for us to replace the bearings on every repair we do.
The technician first dismantles the motor to access the bearings and facilitate any subsequent repairs. The disassembly involves the removal of the fan housing and fan, the removal of assorted nuts, washers, and rods, and the removal of the motor caps to reveal the bearings.
The technician can use a jaw-style puller or a bearing splitter to pull out each bearing from the shaft. A bearing splitter tool applies even, consistent pressure to the bearing, and its narrow profile is best for tight spaces where a jaw-type puller won't work. The bearing splitter can be used with a hydraulic tool as well for another removal option.

Your facility becomes capable of eliminating downtime as well as cutting costs from the industrial service and repair history.
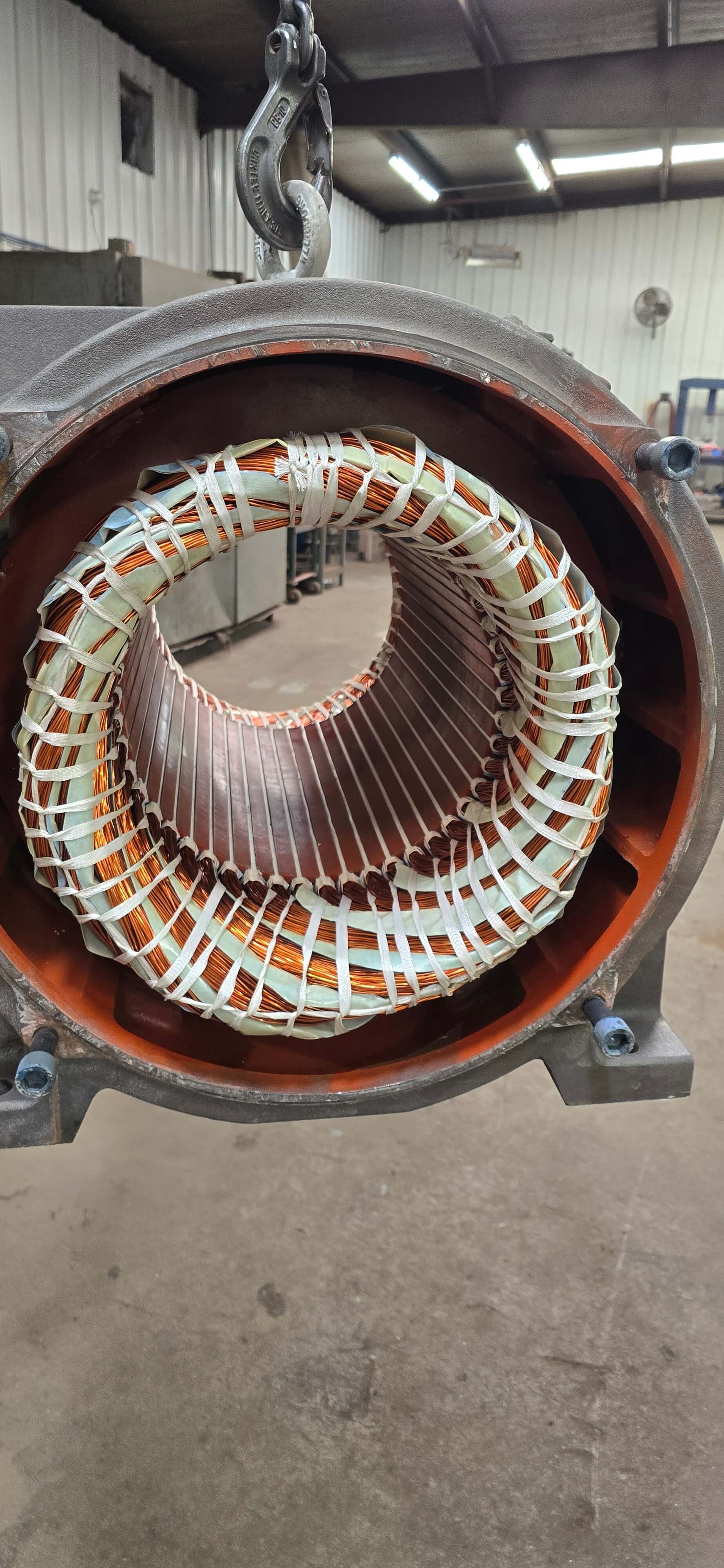

A rotating element, such as a rotor or DC armature, has to be balanced extremely accurately. An imbalance of weights causes wobble, and the result is vibration and stability at lower speeds, which tends to be serious. Unbalance can lead to a variety of failures in the rotating elements, including the following:
Static balance equates to no turning force. When statically balanced, the center of gravity coincides with the axis of rotation. This holds the equipment firm and level without the requirement of force. Balancing guarantees the machine remains stable and immobile.
In dynamic balance, the gear turns without generating centrifugal force or needing force to sustain rotation. The turning helps to sense and correct imbalance.
Dynamic balancing rotates a motor at top speed. Technicians use electronic devices to measure imbalances. Based on this information, they make weight adjustments at certain points to bring the motor back to balance and eliminate vibration. This shifts the motor's center of mass to its axis of rotation.
Dynamic balancing is necessary for many motor components, ranging from the fan to the shaft to the rotor. Basically, if the component spins, it will need dynamic balancing to perform at its best and extend the life of the motor.
In an industrial motor, the rotor should especially be dynamically balanced. The rotor is the major moving part of a motor, it revolves in reaction to the torque produced as a result of interactions between the motor's windings and its magnetic field. Overheating, mounting errors and electromagnetic stresses like vibration and electrical noise can all be causes of the rotor's imbalance.
Dynamic balancing of an industrial motor usually involves procedures like suspending a specific weight at a certain angle, making precise stationary measurements, powering the motor, accelerating it to operating speed, and then utilizing the measurements to guide the application of permanent weights for correct balance and alignment.
